Metabolic acidosis is a medical condition that occurs when there is an accumulation of acid in the body.
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme Borreliosis is a common vector-borne disease which is commonly caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and rarely, Borrelia mayonii.
Vitamin deficiency is a condition that occurs when the body does not receive enough vitamins to function properly.
Enteric organisms are the major causes of gastroenteritis. There are approximately 100 trillion bacteria in the intestine of an average human.
Calprotectin is a sensitive biomarker for gastrointestinal tract inflammation. It is a non-invasive method
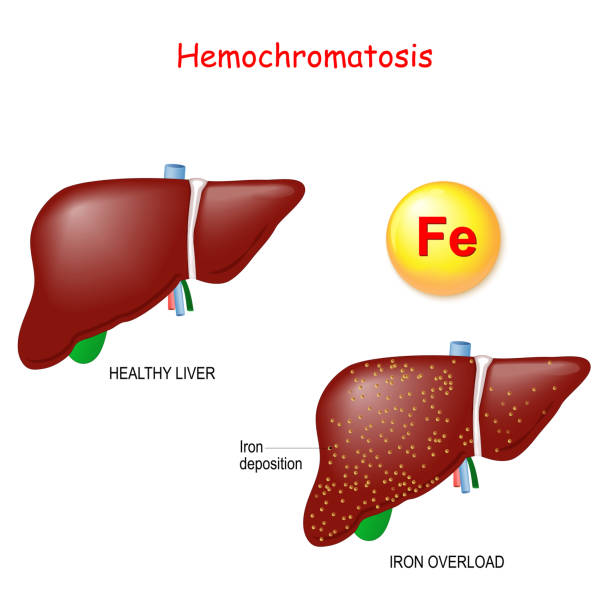
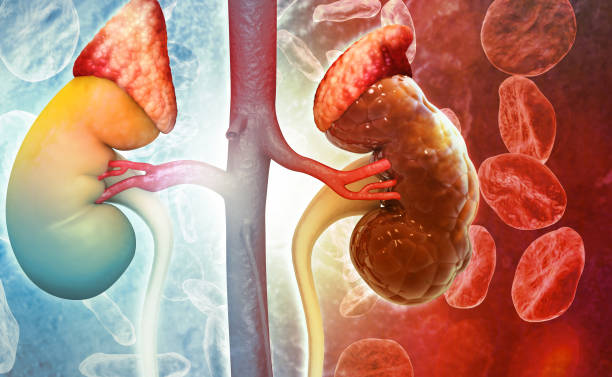
Hemochromatosis, often known as “iron overload,” is a condition where the body accumulates too much iron.
Liver disease can be inherited (genetic) and can also be a result of several underlying causes.
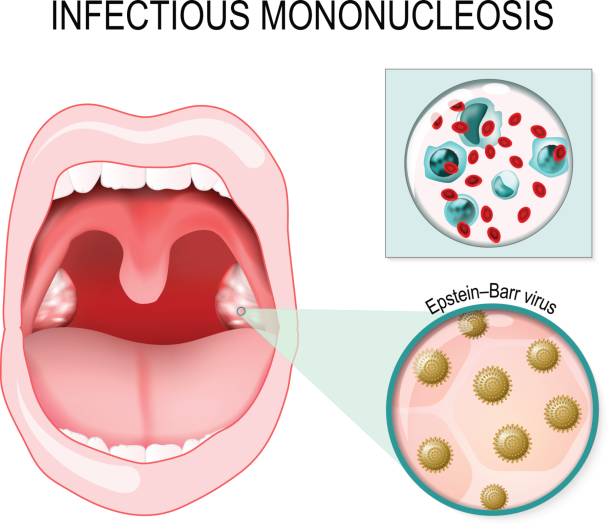
Infectious Mononucleosis, also known as the Kissing Disease is an illness that is caused by the Epstein Barr Virus (EBV).
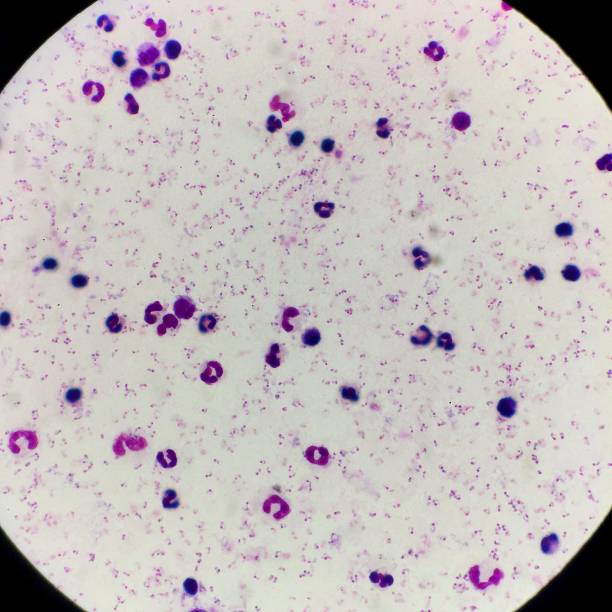
Malaria is a major infectious disease that continues to furnish challenges to population health and healthcare systems worldwide, especially in developing countries.
According to data that was released in 2019, approximately 229 million malaria cases and 409,000 deaths occurred worldwide.
Malaria has similar symptoms to other febrile illnesses such as typhoid. Meanwhile, several people self-diagnose based on the symptoms they exhibit. The availability of over-the-counter antimalaria drugs makes this wrong practice a quick option. Hence, multi-resistance to antimalarial drugs occurs, and when a person is truly infected with malaria, the available drugs become impotent. Also, misdiagnosis of malaria leads to delayed treatment of the actual illness.
Laboratory diagnosis is the most reliable and accurate way to ascertain the presence of malaria parasites in the blood thus helping to distinguish malaria from other febrile illnesses. Laboratory diagnosis of malaria includes a Rapid Diagnostic Test which indicates the presence or absence of malaria infection, a Blood Smear Microscopy Test for confirmation and parasite count, and Parasite Density which helps to monitor the patient’s response to treatment. Other additional tests include PCR to identify parasite species, Complete Blood Count and Blood Glucose Test to check for other complications.
Prompt and correct diagnosis is vital for the effective control of malaria cases to lessen morbidity and mortality caused by delayed or poor management of patients.
Accurate laboratory diagnosis of Malaria will ultimately help to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of the malaria parasite. Say no to misdiagnosis, we’ve got you covered.
For an accurate and reliable diagnosis, visit MedBioTech.
References:
my.clevelandclinic.org
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
www.who.int
Typhoid Fever is a life-threatening infection caused by the bacterium Salmonella Typhi. In a report by the World Health Organisation
Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis is also known as Angiocentric Lymphoma. It is a rare precancerous condition which is triggered by the Epstein- Barr Virus (EBV) infection.
Primary Biliary Cholangitis, previously known as Primary Biliary Cirrhosis, is a chronic disease caused by damage to the bile duct in the liver.
Urinary Tract Infection is the infection of one or more areas of the urinary system. The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Urinary Tract Infection is caused by the presence and multiplication of unwanted bacteria in the urinary tract.
When too much fibrous tissue grows in the retroperitoneal area, which is the region between the stomach and intestines, it results in retroperitoneal fibrosis, also known as Ormond’s disease.
Hypothyroidism is a common endocrine disorder that results from the deficiency of the thyroid hormone. The thyroid gland, when unable to produce a sufficient amount of thyroid hormone into the blood, slows down the body’s metabolism (breakdown of food).
Autoimmune pancreatitis is a rare condition in which the immune system attacks the healthy cell of the pancreas thereby causing inflammation of the pancreas.
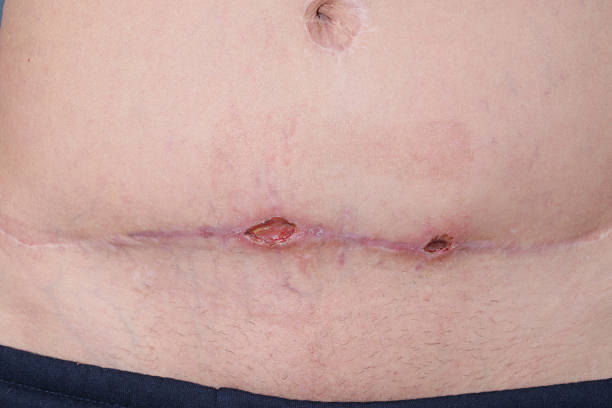
Any surgery that results in a break in the skin can cause an infection, despite the numerous safeguards and protocols in place to prevent infection. These infections are known as Surgical Site Infections.
Pertussis, also known as Whooping Cough, is an highly contagious bacterial respiratory infection. It only occurs in humans. Even though the average age of cases is over 6 years old, 10-15% of all pertussis cases in infants under 6 months old occur, and over 90% of deaths occur in this age group.
Noma disease, also known as Cancrum oris, is a rapidly progressing, flesh- eating infection of the oral cavity. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) globally, it has a mortality rate of 90%.