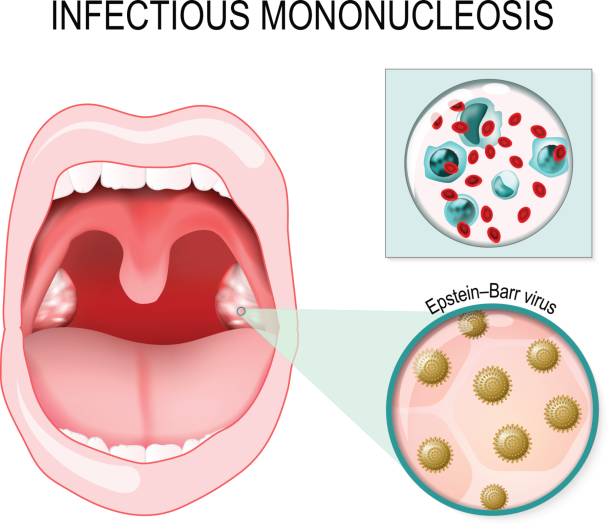
Infectious Mononucleosis, also known as the Kissing Disease is an illness that is caused by the Epstein Barr Virus (EBV). Aside being one of the most common human viruses found all over the world, EBV is a contagious virus.
Infectious Mononucleosis spreads through bodily fluids (primarily saliva) by kissing, sharing foods and drinks, sharing eating and drinking utensils, sharing toothbrushes and having contact with toys and things children have drooled on. Also, it can spread through blood and semen during sexual contact, organ transplantation and blood transfusion.
EBV probably plays a role in the development of some cancers, including nasopharyngeal cancer and lymphomas.
The symptoms of Infectious Mononucleosis may take few weeks to appear. These symptoms include rash, inflamed throat, fatigue, swollen liver, headaches, swollen tonsils, fever, lymph nodes in the neck and enlarged spleen.
Diagnosing Infectious mononucleosis can be quite challenging because its symptoms are similar to other illnesses. However, it can be confirmed with PCR and Complete Blood Count.
Unfortunately, there are no vaccines to protect against Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) infection. Meanwhile, preventive measures includes not kissing, not sharing food, drinks, eating utensils, drinking utensils and toothbrushes with people who are infected.
This is one reason to make going for frequent medical checkup your priority. Visit MedBioTech for reliable laboratory tests and diagnosis.
References:
www.cdc.gov
emedicinehealth.com