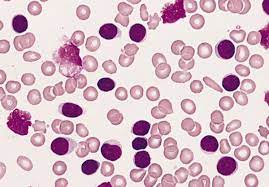
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood and bone marrow that affects the lymphocytes and progresses slower than any other type of leukaemia. It is common leukaemia in adults but rarely seen in children. Globally, 904,000 people were affected with 60,700 deaths in 2015.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia is a result of mutations in the DNA of blood-producing cells. Meanwhile, the actual cause of this mutation is unknown. Some risk factors of this condition are age, race (white), family history of blood and bone marrow cancers, exposure to chemicals and insecticides, exposure to Hepatitis C virus, and any condition that causes the production of excess lymphocytes.
Early on, there are no typical symptoms of CLL. Meanwhile, as time goes on, certain symptoms become evident such as lymphadenopathy, night sweats, difficulty in exercising, frequent infections, fatigue, fever, weight loss, enlarged painless lymph nodes and anaemia.
The diagnosis of CLL is done by Blood Tests (Full Blood Count with Differential), Flow Cytometry, Biomarkers (CD5 and 23) and Array-based Karyotyping.
CLL is incurable as there is no available means of curing it yet. It can instead be controlled or treated with stem cell transplant, targeted therapy, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
These tests are available at MedBioTech Laboratory.
References:
emedicine.medscape.com
en.m.wikipedia.org
www.mayoclinic.org