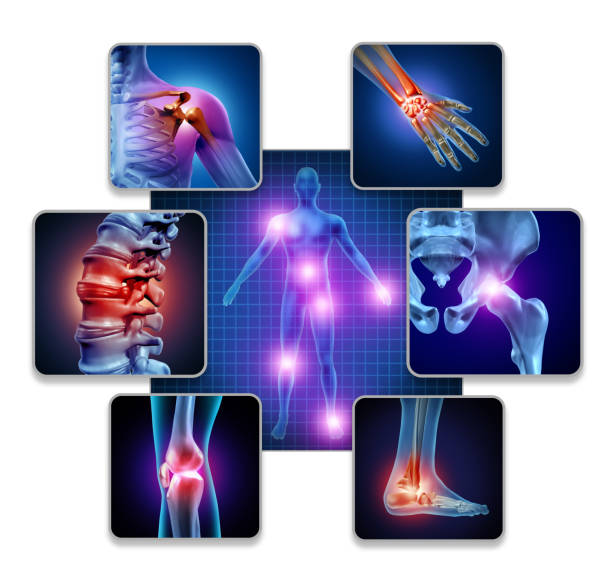
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder which occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s healthy cells. This chronic inflammatory disorder can affect more than just the joint but may also have effect on the nerve tissues, skin, eyes, bone marrow, heart, salivary gland, kidney and blood vessels.
The cause of this process of an immune system attack is not yet known. Meanwhile, some risk factors that can increase the incidence of rheumatoid arthritis are gender, age, family history, smoking and obesity.
Some of the signs that are seen in rheumatoid arthritis are fatigue, fever, loss of appetite, weight loss, stiffness of joints, joint tenderness, joint pain, joint swelling and joint redness.
The complications of rheumatoid arthritis include osteoporosis, rheumatoid nodules infections, heart problems, abnormal body composition, lung diseases and lymphoma.
Imaging tests which include MRI and ultrasound tests can be used to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis. Also, laboratory blood tests such as Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), C- reactive protein (CRP) level, Rheumatoid Factor, and Anti-cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (Anti-CCP) Antibodies are effective in diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis.
Medication, therapy, surgery and maintenance of a healthy lifestyle are considerable ways of treating rheumatoid arthritis.
Visit MedBioTechLab for your laboratory screenings to aid the early detection of rheumatoid arthritis.
References:
www.cdc.gov
www.mayoclinic.org
www.medicalnewstoday.com