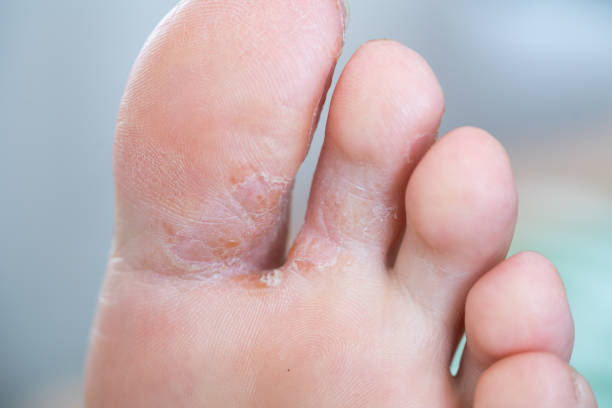
Athlete’s Foot, otherwise known as Tinea Pedis, is an infection of the skin and feet that can be caused by different fungi. Meanwhile, the major causative fungus is the dermatophyte Trichophyton which exists harmlessly on human skin but multiplies rapidly under damp conditions.
Although any part of the foot can be affected, the most affected parts are the spaces between the toes. Athlete’s Foot can be a chronic infection that recurs frequently. It can sometimes spread to the hands in a condition known as Tinea Manuum. Tinea Pedis is contagious as it is transmitted through contact with fungi in infected skin scales, damp areas, towels or shoes.
Anyone can get Athlete’s Foot. Some factors that pose greater risks include heavy sweating, frequently wearing enclosed footwear, minor skin injury on the foot, nail injury, walking barefooted or infected mats, rugs, clothes and shoes.
The signs of Tinea Pedis are red itchy scales between the toes, blisters, skin inflammation, skin cracking and crumbly toenails. Athlete’s foot can lead to complications such as secondary bacterial infection and infections of the lymphatic system.
The laboratory diagnosis of Athlete’s Foot is by microscopic examination of skin scrapings from the affected part of the foot.
To prevent Tinea Pedis, the nails should be clipped short and kept clean always, the feet should be kept clean and dry always, socks should be changed regularly, tight-fitting footwear should be taken off frequently and walking barefoot in public places should be avoided.
At MedBioTechLab, we offer a reliable diagnosis of Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis). Visit us if you notice any of these symptoms.
References:
www.cdc.gov
www.healthline.com
www.mayoclinic.org
www.medicalnewstoday.com