Tuberculosis is an ongoing chronic infection that is caused by a bacterium named “Mycobacterium tuberculosis”. This bacterium mainly affects the lungs. Meanwhile, other organs are sometimes infected (such as the kidneys, spine and brain).
Tuberculosis is the most common cause of infection-related death worldwide. In 1993, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared tuberculosis a global public health emergency.
There are three major stages of tuberculosis, the exposed stage, the latent tuberculosis infection stage and the active tuberculosis disease stage.
When an infected person coughs, sneezes, speaks, sings or laughs, tuberculosis is transmitted through the droplets. A child with an weak immune system (due to HIV, diabetes or immune suppressing drugs), a child living with a person who has tuberculosis, an homeless child or one who comes from a tuberculosis infested country is at risk of getting paediatric tuberculosis.
Symptoms of tuberculosis in children are fever, weight loss, poor growth, cough, chills, and pain in chest, blood in sputum, weakness, tiredness, loss of appetite and night sweats.
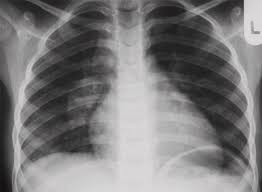
Laboratory diagnoses for detecting tuberculosis are tuberculin skin test, AFB staining technique, Mycobacterium culture, biopsy of the abnormal gland, chest x-ray, nucleic acid probes, immunoassay and serology. To prevent tuberculosis, a child’s exposure to infected people should be reduced. Also, early diagnosis and treatment of latent tuberculosis saves lives.
Visit MedBioTechLab for your laboratory tests for early diagnosis of Tuberculosis.
References:
emedicine.medscape.com
www.urmc.rochester.edu